Monitor Transriptional Activity With Fluorescent TF Reporter Lentivirus
Published On 01/20/2025 12:40 PM
Illuminate Your Research with Our Leading-Edge Lentiviral Reporters!
Biohippo is partnering with LipExoGen to provide over 100 unique transcription factor and signaling pathway lentiviral reporters. Our ever-growing catalog is the largest in the world, ensuring that researchers can find a reporter for virtually any signaling pathway under study.
Find Your Reporter Lentivirus In Our Growing Catalog >>
Transcription Factor & Signaling Pathway
The transcription signaling pathway is a vital cellular mechanism through which external and internal signals regulate gene expression. It involves a series of molecular interactions that activate or repress transcription of specific genes in response to stimuli:
1. Signal Reception:
Signals, such as hormones, growth factors, or stress, bind to specific cell-surface or intracellular receptors.
2. Signal Transduction:
Signal transduction pathways relay the signal from the receptor to the nucleus via intermediates like kinases, secondary messengers, or adaptor proteins.Example: In the MAPK pathway, a cascade of kinases transmits the signal to transcription factors.
3. Transcription Factor Activation:
Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to response elements. They act as activators or repressors of transcription.Example:
NF-κB: Activates immune response genes.
p53: Regulates genes involved in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Transcription factors are activated through phosphorylation, conformational changes, or ligand binding. This allows them to bind specific response elements in DNA.
4. DNA Binding and Transcriptional Regulation:
Activated transcription factors bind to response elements, which are short DNA sequences in the promoter or enhancer regions of target genes and serve as binding sites for transcription factors. This facilitates or inhibits the assembly of the transcriptional machinery, including RNA polymerase II.
5. Gene Expression:
RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA from the DNA template. The mRNA is then translated into protein, mediating the cellular response to the original signal.Example Pathway: NF-κB Signaling >> NF-κB Reporter Lentivirus
1. Signal: Pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α) bind to cell-surface receptors.2. Transduction: The receptor activates the IKK complex, which phosphorylates IκB (an inhibitor of NF-κB).
3. Transcription Factor Activation: NF-κB is released and translocates to the nucleus.
4. Binding to Response Element: NF-κB binds to κB sites in DNA, initiating transcription of target genes.
Importance of Monitoring Transcriptional Activity
Understanding Cellular Responses:
Transcriptional activity reflects how cells respond to external and internal signals, such as hormones, stress, or environmental changes.Monitoring transcription reveals how cells adapt or malfunction in disease states.Drug Discovery and Development:
Screening for compounds that modulate specific transcriptional pathways is a cornerstone of drug development. For example, identifying inhibitors of NF-κB activity can lead to treatments for inflammatory diseases and cancer.Disease Mechanisms:
Aberrant transcriptional activity is a hallmark of many diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic syndromes. Monitoring transcriptional activity helps unravel the molecular underpinnings of these conditions.- Cancer: Dysregulated TFs like p53 (tumor suppressor) or Myc (oncogene) contribute to uncontrolled cell growth and survival.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Overactivation of TFs like NF-κB can lead to chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Abnormal activity of TFs such as CREB is linked to cognitive disorders and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Metabolic Disorders: TFs like PPARs (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors) regulate lipid and glucose metabolism, and their dysregulation can lead to diabetes and obesity.
Transcription Factor (TF) Reporter Lentiviruses:
LipExoGen's Transcription Factor (TF) Reporter Lentiviruses are engineered tools that monitor transcriptional activity by integrating a DNA construct containing transcription factor response elements, a minimal promoter, and a reporter gene (e.g., GFP, RFP, or luciferase) into the host cell genome. Upon activation of the target signaling pathway, the corresponding transcription factor binds to the response elements, initiating reporter gene expression. The reporter output is then measured as fluorescence or luminescence, providing a real-time and quantitative readout of transcriptional activity. This stable integration allows long-term monitoring of transcriptional dynamics in various cell types, including dividing and non-dividing cells.
Lentiviral reporters offer several advantages, including stable genome integration for long-term studies, high sensitivity, and specificity through pathway-targeted response elements. They are versatile, effectively transducing a wide range of cell types, including primary and stem cells, which are typically hard to transfect. Additionally, these reporters enable real-time monitoring and quantitative analysis of transcriptional activity, with single-cell resolution using fluorescent markers or high-throughput screening using luminescent reporters. This makes them powerful tools for studying gene regulation, pathway dynamics, drug screening, and cellular responses under various conditions.
Why Choose Us?
Unrivaled Sensitivity – LipExoGen Reporter lentiviral particles are made using a novel vector platform based on the third generation system. The transcription factor’s response elements are arranged as DNA tandem repeats upstream of the minimal TATA promoter-driven reporter, and downstream of an optimized mini enhancer. When the signal pathway/TF is activated, the mini enhancer synergizes with TF binding to the response elements (up to 8 repeats in some products, depending on strength of reporter activation) to amplify expression of the fluorescent (GFP/RFP) or luciferase (Luc) reporter, with minimal enhancement of background. As a result, the reporter system provides a highly sensitive readout for signaling pathway or specific transcription factor activation in human and mouse cells.
Easily Establish Stable Reporter Cell Lines – The reporter lentiviral particles are ultra-purified and concentrated to high-titer by PEG purification and sucrose gradient centrifugation to allow for efficient transduction of difficult-to-transfect cells, including primary and/or freeze-thawed cells. Stable cell lines are easily generated through puromycin or blasticidin selection.
Discovery Made Easy – Signal pathway or specific transcription factor activity can be detected by fluorescence, making LipExoGen TF Reporter lentiviral particles more practical than traditional luciferase reporters and/or biochemical assays. Pathway/TF activation can be readout by flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy in living cell cultures, providing more versatility in data acquisition for labs with different instruments.
Best Value – LipExoGen lentiviral particle products are made using optimized lentiviral vectors developed in-house, which allows us to provide the highest quality products while retaining competitive prices. These high-titer lentiviral particles feature a highly sensitive fluorescent reporter system which has been validated to read out the indicated transcription factor activity.
Completely Customizable – You can easily request a modified version of the lentiviral reporter, such as a dual-reporter or a different reporter not listed on our website, by contacting us.
Find Your Transcription Factor/Signaling Pathway in Our Growing Catalog >> View All
Step 1: Look up the transcription factor/signaling pathway of interest in the list below (in alphabetical order):| Symbol | Product Name | Cat No. |
| Amino acid response (eIF2α/ATF4) pathway | AARE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400033 |
| Androgen receptor (AR) signaling pathway | AnRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400041 |
| JNK signaling pathway | AP1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400017 |
| NRF1/2 antioxidant pathway | ARE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400016 |
| ATF2/JNK Pathway | ATF2 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| ATF4/Amino acid response | ATF4 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400044 |
| ATF6 | ATF6 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400092 |
| BMP Signaling Pathway | BRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400070 |
| C/EBP-α⋅PPAR signaling pathway | C/EBP-α Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400054 |
| C/EBP-β⋅PPAR signaling pathway | C/EBP-β Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400029 |
| CAR1 | CARE Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| Cell cycle (phases) | Cell Cycle Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400048 |
| Carbohydrate metabolism (ChREBP/MLXIPL) | ChoRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400040 |
| CLEAR gene network | CLEAR Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400053 |
| cMYC | c-MYC Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400006 |
| cAMP/PKA pathway (CREB-1) | CREB Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400013 |
| CSL (CBF1/RBP-Jk) | CSL Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| E2F transcription factors | E2F Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400022 |
| EGR1 | EGR1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400079 |
| Estrogen receptor (ER) signaling pathway | ERE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400042 |
| ERG | ERG Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400090 |
| ER stress response | ESRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400031 |
| Forkhead (FKH) Transcription Factors | FKH Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400035 |
| FOXA1/2 | FOXA1/2 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| FOXC2 | FOXC2 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400057 |
| FOXC2 & ETS family members synergistic activity | FOXC2/ETS Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| FOXD1 | FOXD1 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| FOXF1/FARE | FOXF1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400087 |
| FOXH1/TARE | FOXH1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400086 |
| FOXK1 | FOXK1 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| FOXM1 | FOXM1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400055 |
| FOXN1 | FOXN1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400058 |
| FOXO1/IRE | FOXO1/IRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400036 |
| FOXO3 | FOXO3 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400037 |
| FOXQ1 | FOXQ1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400093 |
| Farnesoid X receptor pathway | FXRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400023 |
| GAL4-DBD for PPI and two-hybrid assay | GAL4 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400034 |
| IFNγ/JAK/STAT1 pathway | GAS Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400020 |
| GATA3 | GATA3 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400072 |
| Calcium signaling | GECI Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400050 |
| GLI/Hedgehog pathway | GLI Reporter Lentivirus (Hedgehog Pathway) | BHV19400011 |
| Nuclear hormone receptor pathway | GRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400021 |
| Hypoxia/HIF pathway (HIF-1α) | HIF1a Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400005 |
| Hypoxia/HIF pathway (HIF-2α) | HIF2a Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400025 |
| HNF1β | HNF1β Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400074 |
| HNF4α | HNF4α Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| HOXA9 | HOXA9 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400075 |
| HOXB1 | HOXB1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400076 |
| Androgen Receptor (AR) Pathway (HOXB13) | HOXB13 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400059 |
| Heat shock response pathway (HSF-1) | HSE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400008 |
| IL-1 signaling pathway | IL1RE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400085 |
| IL-2 | IL-2 Promoter Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| JAK/STAT pathway | ISRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400019 |
| KLF5 | KLF5 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400088 |
| LRH1 | LRH1 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| LXR pathway | LXRE Reporter Lentivirus (LXR) | BHV19400030 |
| MAF Signaling Pathway | MARE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400062 |
| MEF2 Transcription Factors | MEF2 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400063 |
| MITF | MITF Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| Metal response pathway (MTF-1) | MRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400038 |
| MYB | MYB Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400056 |
| MyoD/Myogenic factors | MyoD Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400045 |
| NANOG | NANOG Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400095 |
| NeuroD1 | NeuroD1 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| Calcium/NFAT pathway | NFAT Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400001 |
| NFE2 | NFE2 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400064 |
| NFκB (p65 homodimer) | NFκB (p65) Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400065 |
| NFκB signaling pathway | NF-κB Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400002 |
| NFκB and AP1 | NFκB-AP1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400061 |
| NKX2.5 | NKX2.5 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400080 |
| N-MYC | N-MYC Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| Notch signaling pathway | NOTCH Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400009 |
| NPAS4 | NPAS4 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| NR2F2 | NR2F2 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400091 |
| NR3C2 | NR3C2 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| NUR/RXR | NUR/RXR Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| NR4A1 | NurRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400094 |
| OCT4 | OCT4 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| p52:RelB heterodimer | p52:RelB Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| Apoptosis/p53 signaling pathway | P53 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400007 |
| PAX2 | PAX2 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400082 |
| PAX6 | PAX6 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| PAX8 | PAX8 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| Pit-1/PouF1 | PitRE Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| PPARα | PPAR-alpha Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400068 |
| PPAR signaling pathway | PPAR-gamma Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400027 |
| PPARδ | PPARδ Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400073 |
| PPAR signaling pathway | PPRE Reporter Lentivirus (Pan) | BHV19400026 |
| Progesterone Signaling Pathway | PRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400069 |
| PROP1 | PROP1 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| PU.1 | PU.1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400077 |
| Pregnane X receptor (PXR) | PXRE Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| RAR signaling pathway | RARE/DR5 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400039 |
| Internal Ctrl | Renilla Luciferase Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400049 |
| N/A | Reporter Negative Control Lentivirus | BHV19400066 |
| N/A | Reporter Positive Control Lentivirus | BHV19400067 |
| ROR transcription factors | RORE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400028 |
| RORα | RORα Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| RORγt | RORγt Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400060 |
| RUNX1 | RUNX1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400078 |
| RXR signaling pathway | RXRE/DR1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400043 |
| SIX1 | SIX1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400089 |
| TGF-β signaling pathway | SMAD2/3 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400012 |
| SOX2 and OCT4 | SOX2-OCT4 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400083 |
| MAPK/ERK pathway | SRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400024 |
| Lipogenesis pathway (SREBP1) | SREBP1 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400004 |
| Lipogenesis pathway (SREBP2) | SREBP2 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400018 |
| STAT3 | STAT3 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400003 |
| STAT4 | STAT4 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400051 |
| STAT5 signaling pathway | STAT5 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400014 |
| STAT6 | STAT6 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400052 |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) pathway | T3RE/DR4 Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400046 |
| T-bet | T-bet Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400071 |
| Wnt/β-catenin pathway | TCF/LEF Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400010 |
| Hippo signaling pathway (TEAD/YAP) | TEAD Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400015 |
| TOX1 | TOX1 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| T-Pit & PitX1 | T-Pit/PitX1 Reporter Lentivirus | Available. Inquire Now |
| Unfolded protein response (UPR) | UPRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400032 |
| Vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) | VDRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400081 |
| Xenobiotic stress/AhR signaling pathway | XRE Reporter Lentivirus | BHV19400047 |
Step 2: Add the reporter of your choice
| Reporters (Expressed by pathway activation) | |
| Fluorescent | GFP, RFP, BFP2 |
| Luminescent | FLuc, RLuc, secreted GLuc, red FLuc |
| Enzymatic | SEAP, β-Lactamase |
| Degradable | d2GFP, d2RFP, Luc-CP |
| Dual | GFP or RFP & FLuc |
Step 3: Add your selection marker
| Selection Markers (Constitutively expressed) | |
| Drug Resistance | Puro, BSD, Hygromycin, Bleomycin |
| Fluorescent | GFP, RFP, BFP2, GFP-P2A-Puro/BSD, RFP-P2A-Puro/BSD |
Real-World Applications
Study Temporal Activation of Signaling Pathways
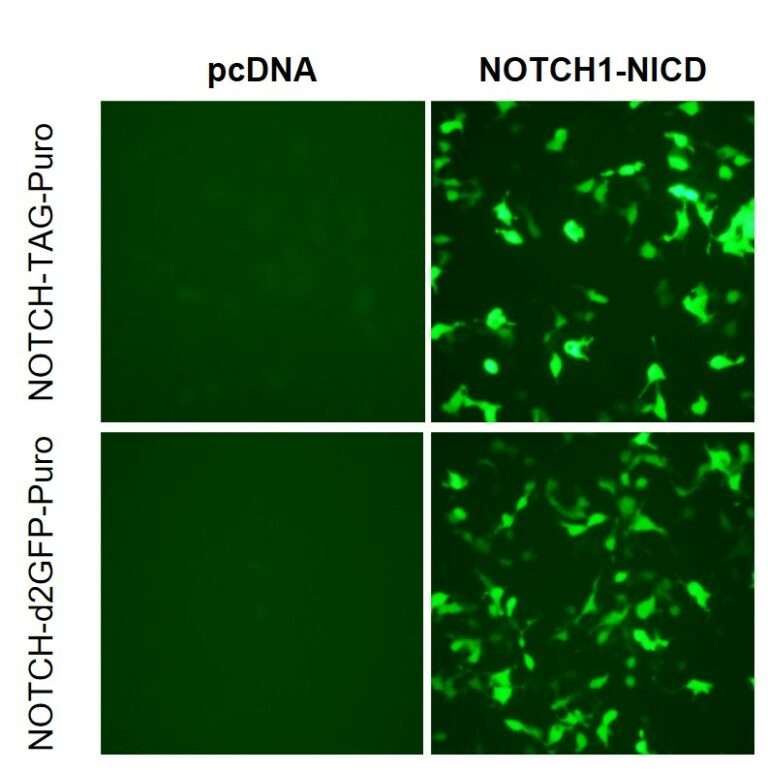
Comparison of NOTCH1 TAG and degradable GFP (d2GFP) reporter plasmids in co-transfection with NOTCH1 NICD. HEK293FT cells were co-transfected with the reporter lentivirus (Cat No. BHV19400009) and cDNA encoding NOTCH1 intracellular domain (NICD) for 24-36hrs. Compared to the traditional GFP reporter (TAG), degradable d2GFP (d2G) shows slightly reduced background and GFP intensity in the cells with overexpressed NOTCH NICD. The degradable reporter could potentially be useful in studying temporal activity of the NOTCH pathway.
Make Stable Cell Lines & Detect Transcriptional Activity on Flow

Assessing BMP Signling in C2C12 cells using flow cytometry: C2C12 cells were infected with 50 ul of BRE-TAR-BSD lentivirs (Cat no. BHV19400070-2) and selected with blasticidin to obtain a stable reporter cell line. The lentiviral construct utilizes tanem repeats of BMP response element (BRE) to drive expression of RFP in response to BMP signaling pathway activation, which was detected on flow cytometry after 24 h incubation with BMP4 (50 ng/ml).

NFAT Reporter Stable Cell Line from Primary Human PBMC: Human PBMC were incubated with NFAT-TAG-Puro lentiviral particles (Cat No. BHV19400001) with 6 ug/mL polybrene for 1 h, followed by spin transduction for 2 h. After culturing for 2 days with IL-2, PBMC were selected with puromycin (0.5-1 ug/ml) for 2 days. Then, PBMC were stimulated with PMA + ionomycin for 8 h, and GFP expression was analyzed by flow cytometry, comparing treated PBMC with those treated with PBS.
Test Drugs & Monitor Transcriptional Activity In Vivo

In vivo tracking of HIF1α activity with luciferase reporters for drug discovery: HCT116 cells were transduced with HIF1α-TAL-Puro (Cat No. BHV19400005-3) and puromycin selected to establishg a stable cell line. The luciferase reporter activity can be detected in vivo using IVIS. A reduction in reporter signal following administration of an HIF1α transcriptional inhibitor (48 h after treatment) depicts how the product could be used for lead validation or to screen for novel HIF1α inhibitors in vivo.
This entry was posted in
Application and Technique Notes
 Loading ....
Loading ....
